In today’s digital world, cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations. With organizations increasingly adopting cloud solutions for storage, data management, and software services, ensuring robust cloud security has never been more critical. The vast number of benefits offered by cloud services—such as flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness—also brings with it significant security risks. From data breaches and hacking attempts to data loss and compliance violations, cloud security concerns are paramount for organizations of all sizes.
This article explores how organizations can improve their cloud security posture by implementing essential practices, technologies, and strategies that mitigate the risks associated with cloud environments.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud security is critical to protect sensitive data and ensure business continuity.
- A comprehensive cloud security framework is essential for implementing effective policies and procedures.
- Strong access controls, encryption, and regular patching are key to improving cloud security.
- Continuous monitoring, employee education, and disaster recovery plans are vital for preventing and mitigating risks.
- Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards is a must for maintaining secure cloud operations.
Why Is Cloud Security Important?
Before diving into how organizations can improve cloud security, it’s essential to understand why it’s crucial. The primary reason for securing cloud environments is that they hold an organization’s most sensitive data, intellectual property, and customer information. A breach of cloud security can result in:
- Data Breaches: Compromise of sensitive information, such as personal identifiable information (PII), financial records, and intellectual property.
- Financial Loss: Security incidents can lead to direct financial losses, as well as penalties for non-compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Reputation Damage: A cloud security breach can severely damage an organization’s reputation and lead to the loss of customers and trust.
- Legal Consequences: Violations of industry-specific regulations, such as healthcare or finance, can result in lawsuits and penalties.
With these threats in mind, organizations need to adopt a proactive approach to securing their cloud environments. Here are key steps organizations can take to improve their cloud security.
How Can Organizations Improve Their Cloud Security?
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Strong Authentication | Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure only authorized users access cloud resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. |
| Encrypt Data | Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to protect it from interception or theft while being stored or transmitted across networks. |
| Monitor and Audit Cloud Activity | Continuously monitor cloud environments for suspicious activities. Use logging and auditing tools to track user actions and identify potential threats early. |
| Implement Access Controls | Use the principle of least privilege by limiting user access to only the resources they need. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. |
| Use Cloud Security Tools | Deploy specialized cloud security tools like cloud access security brokers (CASBs), firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and anti-malware solutions tailored for cloud environments. |
| Regularly Update and Patch Systems | Ensure that all cloud systems, applications, and services are regularly updated with the latest security patches to prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities. |
| Secure APIs and Integrations | APIs and integrations with third-party services should be secured with proper authentication, authorization, and encryption to avoid data leaks or breaches. |
| Implement a Zero-Trust Model | Adopt a zero-trust security framework where no entity, whether inside or outside the network, is trusted by default. All access must be verified. |
| Backup Data Regularly | Regular backups of critical data in a secure manner ensure that organizations can recover quickly in case of data loss due to an attack or system failure. |
| Educate and Train Employees | Provide ongoing security awareness training to employees to recognize phishing attacks, enforce safe cloud usage practices, and prevent human error-related breaches. |
| Use Secure Cloud Configurations | Ensure cloud infrastructure is securely configured, following best practices like disabling unnecessary services, securing ports, and minimizing exposed resources. |
| Implement Cloud Disaster Recovery | Develop and implement a cloud-specific disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in case of a cyberattack or cloud service failure. |
| Conduct Regular Security Audits | Periodically perform security audits to assess vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in cloud security strategies. |
| Ensure Compliance with Regulations | Align cloud security measures with relevant compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 to meet industry-specific regulatory requirements. |
| Use a Trusted Cloud Service Provider | Select a reputable cloud service provider with robust security measures, compliance certifications, and clear security practices to reduce risk. |
Adopt a Cloud Security Framework
A well-defined cloud security framework is crucial for establishing clear security objectives, policies, and procedures. Popular frameworks like the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA)’s Cloud Controls Matrix or NIST Cybersecurity Framework provide a set of standards and guidelines to help organizations manage their cloud security risks.
These frameworks help organizations evaluate their current security posture, identify weaknesses, and implement solutions to mitigate vulnerabilities in their cloud environments. By adopting a comprehensive framework, organizations can standardize cloud security practices and ensure they align with industry best practices.
Use Strong Access Management Policies
One of the first lines of defense in cloud security is access control. Many cloud security incidents arise from weak or mismanaged access permissions, where unauthorized users or malicious actors gain access to critical systems or data.
Organizations should:
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing cloud resources. This greatly reduces the chances of unauthorized access.
- Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC allows administrators to assign specific permissions based on a user’s role within the organization. This ensures that employees can only access the resources necessary for their job, minimizing the risk of exposure.
- Regularly Review Access Permissions: Conducting routine access audits ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive cloud data and services.
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
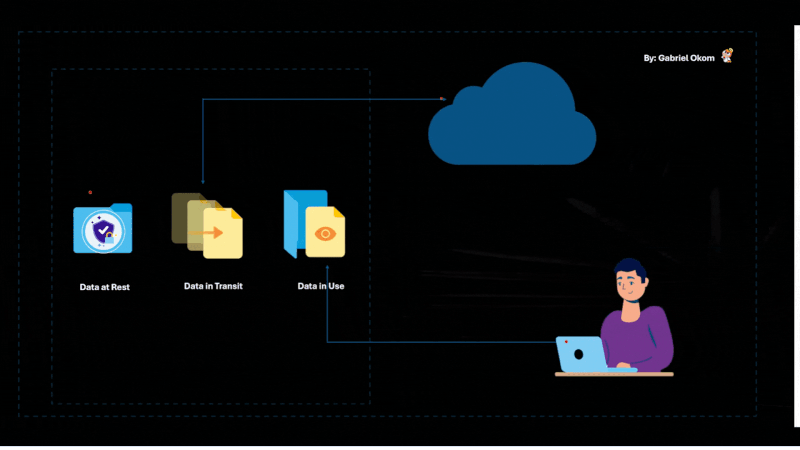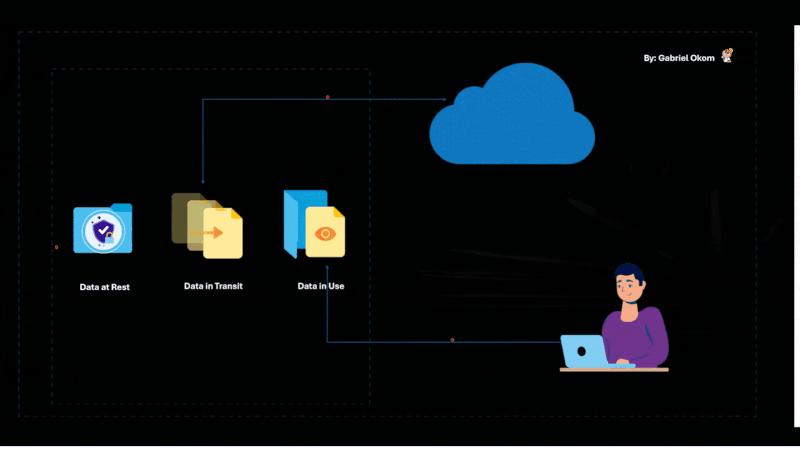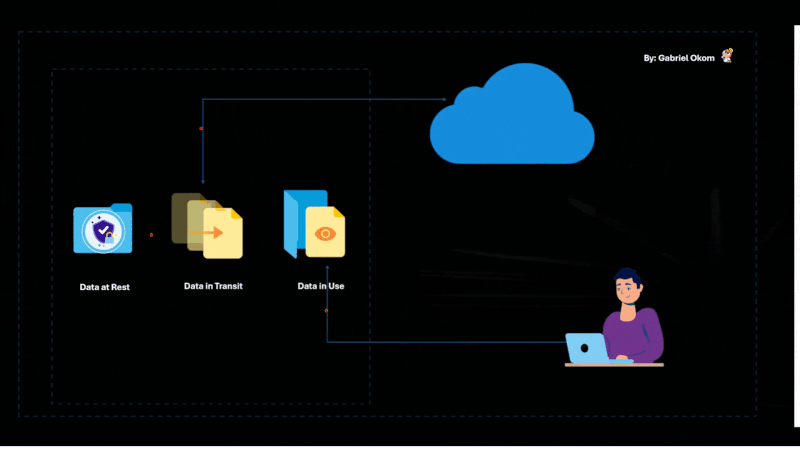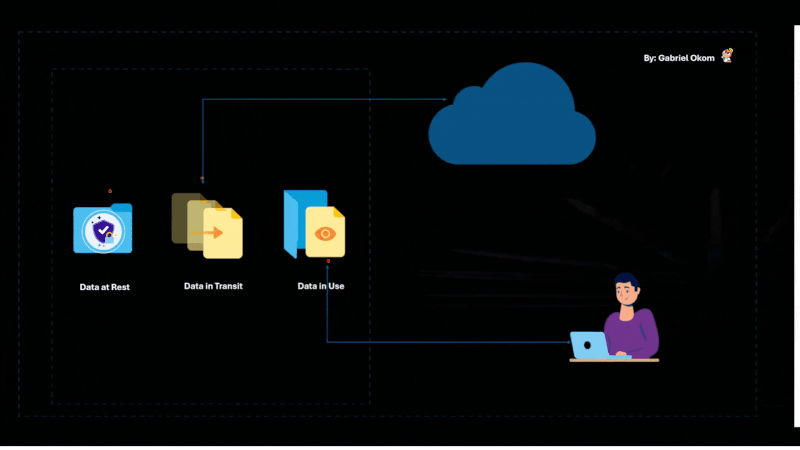
Data encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, especially in a cloud environment. Organizations should implement end-to-end encryption for data both at rest (when stored in the cloud) and in transit (when being transferred over the internet).
Encryption prevents unauthorized users from reading or modifying the data, even if they manage to access the storage or intercept the communication. Ensure that the encryption keys are stored securely and managed appropriately to prevent any potential leaks.
Regularly Update and Patch Cloud Systems
Cloud service providers (CSPs) often provide security updates and patches to address vulnerabilities in their infrastructure. However, it is crucial for organizations to stay up-to-date with security patches and apply them to their systems, applications, and services hosted in the cloud.
Unpatched systems are prime targets for attackers who can exploit vulnerabilities to gain access. To minimize the risk, organizations should implement a regular patch management process and automate updates whenever possible to ensure that critical patches are not missed.
Implement Strong Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
No matter how secure an organization’s cloud environment is, disasters can still occur, ranging from cyberattacks to natural events like fires or floods. In such cases, having a robust backup and disaster recovery plan is essential to ensure business continuity.
Organizations should:
- Perform Regular Backups: Schedule automated backups of all critical data, ensuring that backup copies are securely stored in multiple locations.
- Test Recovery Procedures: Periodically test disaster recovery plans to ensure they are effective and that data can be restored quickly in the event of a breach or system failure.
- Utilize Cloud-native Backup Solutions: Many cloud providers offer native backup solutions that are optimized for their platforms. These solutions are often more efficient and secure than third-party alternatives.
Monitor and Audit Cloud Environments Continuously
Ongoing monitoring of cloud environments is essential to detect security threats early and prevent potential breaches. Automated monitoring tools can help organizations identify unusual activities or potential vulnerabilities in real-time.
Consider using:
- Cloud Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools: These tools aggregate and analyze logs from various cloud resources to detect potential security threats and provide actionable insights.
- Cloud-native monitoring tools: Many cloud providers, like AWS CloudTrail or Azure Security Center, offer built-in monitoring tools to track user activity, system events, and security incidents.
Additionally, performing regular audits of your cloud infrastructure helps identify potential gaps in security and compliance, ensuring that security policies and practices are being followed.
Educate Employees About Cloud Security Best Practices
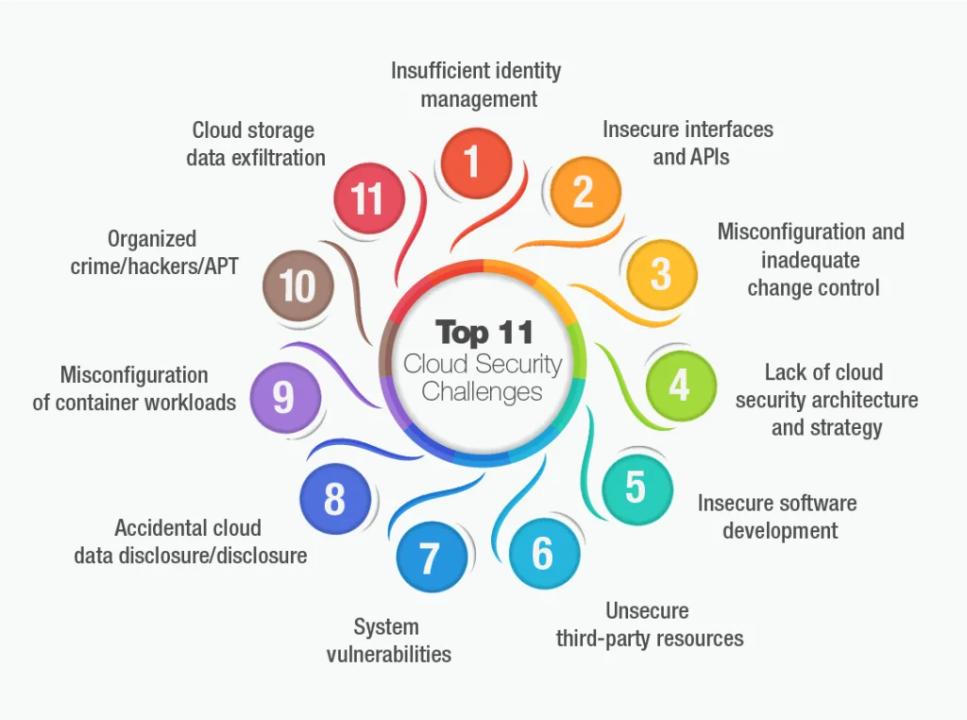
A significant portion of security breaches occurs due to human error, such as falling for phishing scams or misconfiguring cloud services. To mitigate this risk, organizations should focus on educating employees about cloud security best practices, including:
- Recognizing phishing attempts and malicious links
- Understanding the importance of strong, unique passwords
- Reporting security incidents or suspicious activities immediately
Employee training should be a continuous process, with regular updates to account for evolving threats.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards is a critical aspect of cloud security. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS mandate strict security measures for handling sensitive data in the cloud.
Organizations should:
- Stay Informed About Regulatory Requirements: Be aware of the legal and regulatory obligations that apply to your organization’s data.
- Implement Compliance Tools: Many cloud providers offer compliance tools and certifications to help organizations meet regulatory requirements.
- Perform Regular Audits for Compliance: Conduct internal and external audits to ensure that your cloud systems adhere to the necessary compliance frameworks.
Also Read :- Why Is Network Security Crucial for Modern Businesses?
Conclusion
- As organizations increasingly move to the cloud, ensuring robust cloud security is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. By adopting a comprehensive approach to cloud security, including encryption, strong access control, continuous monitoring, and regular employee training, organizations can effectively mitigate security risks and protect sensitive data.
- While cloud service providers offer strong security features, it’s important to remember that cloud security is a shared responsibility. By leveraging the right tools and strategies, organizations can build a secure cloud environment that fosters innovation without compromising on data protection.
FAQs
What is cloud security?
Cloud security refers to the set of policies, technologies, and practices designed to protect data, applications, and services hosted in the cloud from various cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
How do cloud providers ensure security?
Cloud providers offer built-in security measures such as encryption, firewalls, identity and access management (IAM), and security monitoring tools. However, organizations must take additional steps to secure their cloud environments.
Is cloud security the responsibility of the provider or the organization?
Cloud security is a shared responsibility. The cloud provider secures the infrastructure, while the organization is responsible for securing the data, applications, and user access within the cloud.
What are the common cloud security risks?
Common cloud security risks include data breaches, data loss, unauthorized access, misconfigurations, and compliance violations.
What is the best way to secure cloud data?
The best way to secure cloud data is through encryption, strong access control policies, regular backups, and continuous monitoring for suspicious activity.
How does multi-factor authentication (MFA) improve cloud security?
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before gaining access to cloud resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
How often should organizations review their cloud security policies?
Organizations should review their cloud security policies regularly—at least annually or whenever there are significant changes in cloud infrastructure or business needs.